About SCSA Diagnostics
Extensive studies in Sweden show that SCSA-derived DFI values above 27% resulted in almost no IUI pregnancies; in fact, the Southern Sweden Health System will not reimburse a patient for IUI treatment unless the SCSA %DFI is below 27%. Such patients are counseled to try ICSI fertilization.
Dr. Y. Menezo, one of the leading infertility specialists in France, states, "a strict check of sperm is mandatory before all assisted reproduction treatment. Passage from IUI to ICSI must not be automatic. Sperm DNA fragmentation and Decondensation (% HDS), which have only a weak correlation with classical sperm analysis, must be performed after failed IUI cycles, before ICSI"
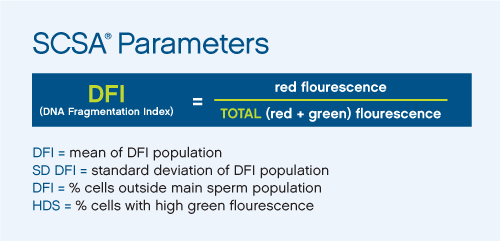
For the SCSA® test, green fluorescing sperm have non-detectable levels of fragmented DNA, while yellow to red fluorescing sperm have moderate to high levels of fragmented DNA, respectively. Moderate to high DNA fragmentation levels found within these red fluorescing sperm are likely beyond the DNA repair capacity of the egg. Measurements from 5000 individual sperm are analyzed by the SCSAsoft software to determine the percentage of the sperm with increased yellow to red color (% DFI), and the % of sperm with nuclear immaturity (% HDS)
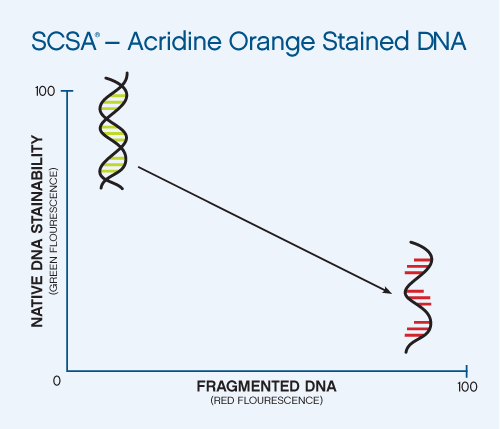
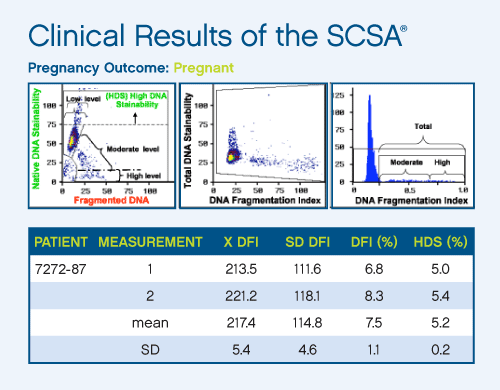
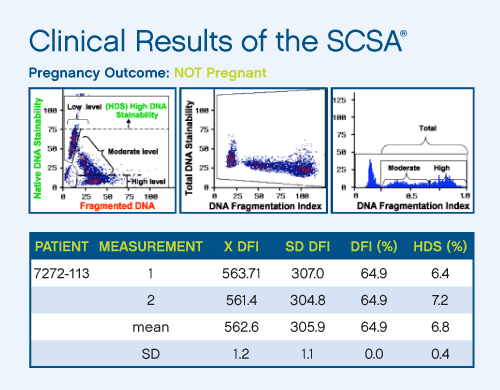
There are five major populations of sperm identified by the SCSA® test:
- Non-detectable DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI): percentage of mature sperm with non-detectable levels of nuclear DNA fragmentation.
- Moderate DFI: percentage of sperm with moderate levels of DNA fragmentation.
- High DFI: percentage of sperm with high levels of DNA fragmentation.
- DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI): the percentage of sperm with moderate and high levels of DNA fragmentation (% Moderate DFI + % High DFI).
- High DNA Stainability (%HDS): the percentage of sperm with immature chromatin. HDS sperm have less chromatin condensation, which leads to increased DNA stainability. Some studies have shown that no pregnancies occurred if the %HDS is above 36% (Menezo)
Selecting sperm for ICSI—by high magnification microscopy
It has been shown that sperm appearing as morphologically normal with the use of the microscopes typically used in an ICSI procedure may in fact carry various structural abnormalities that can only be detected with the use of a higher magnification microscope (Bartoov et al 2002). The primary defect was the presence of sperm head nuclear vacuoles as seen in the above figure. Practically, the use of this high magnification technique takes considerable time and is not considered practical by many embryologists.
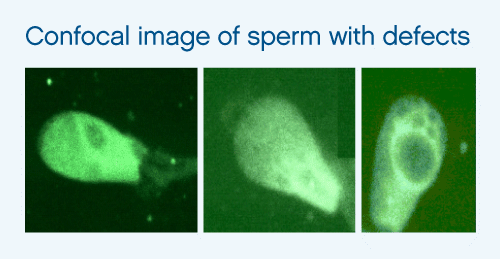
It is of note here that semen samples with a high level of sperm nuclear vacuoles usually have a high %DFI in the SCSA. The sperm in the figure (above) were from a patient with a 35% DFI; the same abnormality has been observed for bull sperm (Karabinus et al). These findings suggest that when such a sample with a high %DFI is seen the couple should consider using high magnification selection of sperm for ICSI.
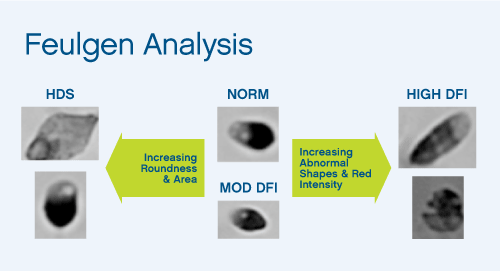
The following three figures are derived from our SCSA laboratory research. A semen sample showed the classical five types of cells: 1) no DNA fragmentation detected (normal), 2) moderate level of DNA denaturation, 3) high level of DNA denaturation, 4) High DNA Stainable region (HDS) and 5) dead cells and debris.
Our flow cytometer can physically sort out each cell type and deposit them on a glass slide. We then further analyzed each cell type by two methods:
1) Stain the cells with Feulgen stain and then analyze the cell shape with a computer image analysis system (20 characters of cell shape).
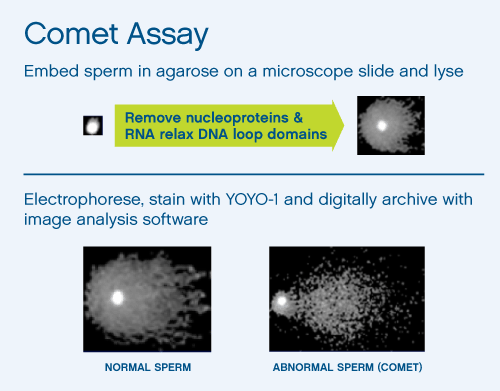
2) Do a Comet assay on these sorted sperm cells. This is a method that pulls broken pieces of DNA out of the nucleus on the glass slide so that the pulled out pieces are seen under the light microscope as an astrological "comet". Cells are scored as positive or negative for comets which equate to fragmented DNA.
Feulgen Analysis Figure: The Norm sperm have good morphology. Importantly, the Mod DFI (moderate level of sperm DNA fragmentation) have the same level of good morphology as the normal sperm. (This is important since an ART technician would not be able to distinguish a sperm with no detectable DNA fragmentatin from those that have moderate levels of DNA fragmentatin).
The High DFI (high levels of fragmented DNA) have poor morphology and have signs of dying.
The HDS sperm have morphology consistent with immature sperm.
COMET ASSAY
Note that a sperm with fragmented DNA (Abnormal sperm) have a "comet tail"
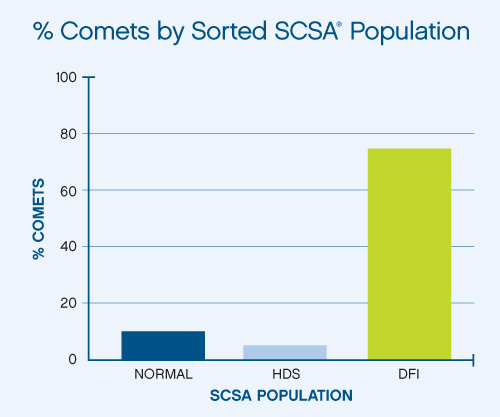
In the lower figure (% Comets by sorted SCSA Population) that the normal and HDS population have low levels of Comets (broken DNA) whereas the SCSA defined DFI sperm have high levels of double strand broken DNA.
 PATIENT INFORMATION
PATIENT INFORMATION CLINIC INFORMATION
CLINIC INFORMATION

